Node.js 原理详解
事件循环模型 Event Loop
调用栈(1)
js
function multiply(a, b) {
return a * b;
}
function square(n) {
return multiply(n, n);
}
function printSquare(n) {
console.log(squre(n));
}
printSqure(4);
调用栈(2)
js
function multiply(a, b) {
throw new Error();
}
function square(n) {
return multiply(n, n);
}
function printSquare(n) {
console.log(squre(n));
}
printSqure(4);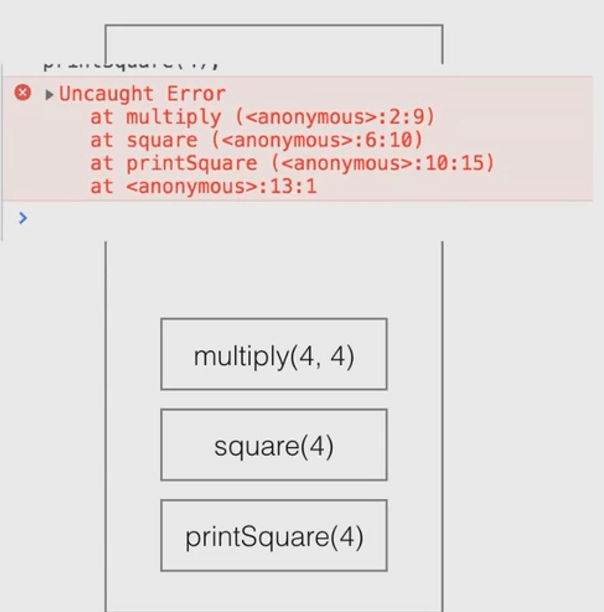
调用栈(3)
js
function fn(a) {
fn(a);
}
fn(1);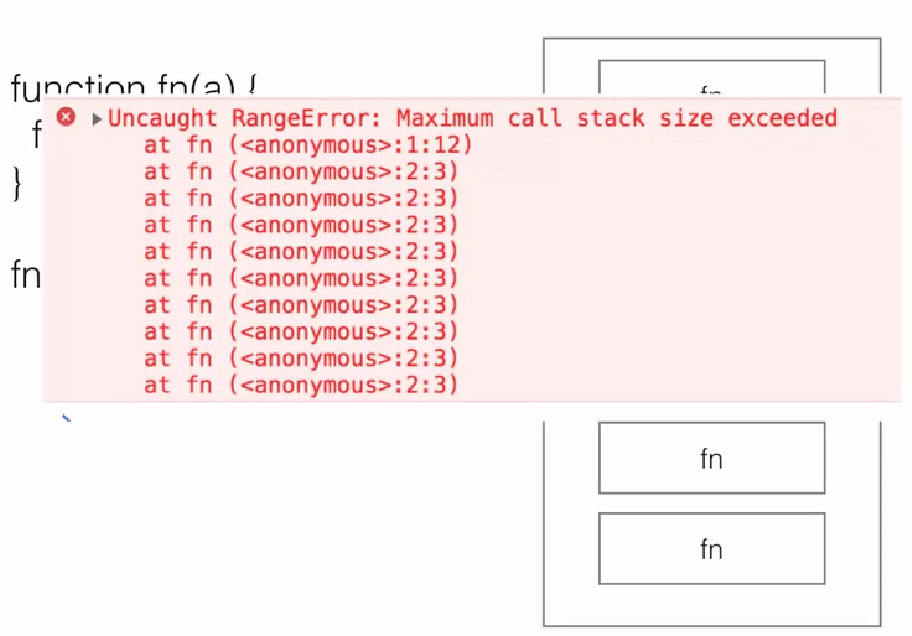
同步调用
js
const fs = require('fs');
fs.readFileSync('./a.txt');
fs.readFileSync('./b.txt');
fs.readFileSync('./c.txt');
console.log('finish');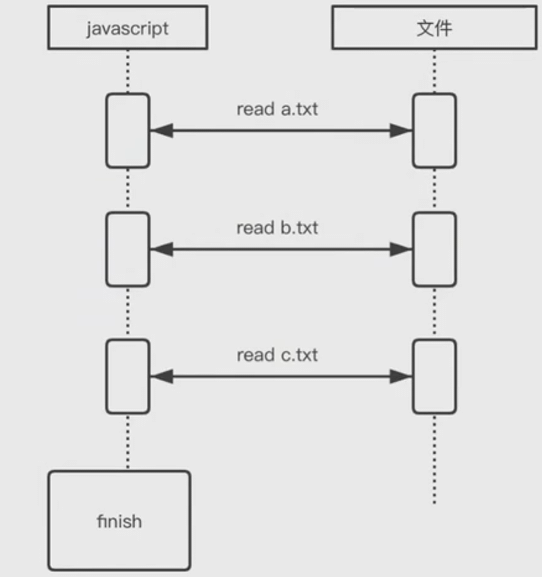
异步调用
js
const fs = require('fs');
fs.readFile('./a.txt');
fs.readFile('./b.txt');
fs.readFile('./c.txt');
console.log('finish');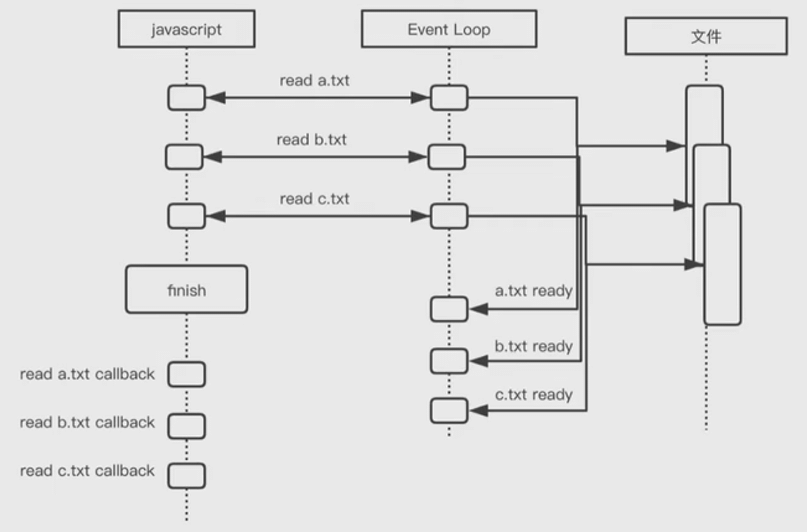
事件循环机制
js
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('timeout');
}, 5000);
console.log('hello');
宏任务与微任务
宏任务
- setTimeout
- setInterval
- js 主代码
- setImmediate(Node)
- requestAnimationFrame(浏览器)
微任务
- process.nextTick
- Promise 的 then 方法
任务队列被分为 1. 宏任务队列 和 2. 微任务队列
微任务队列率先执行, 直到清空
当微任务队列为空时, 执行宏任务队列
事件循环机制
js
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('timeout');
}, 0);
new Promise((resolve) => {
console.log('promise');
resolve();
}).then(() => {
console.log('then');
});
console.log('hello');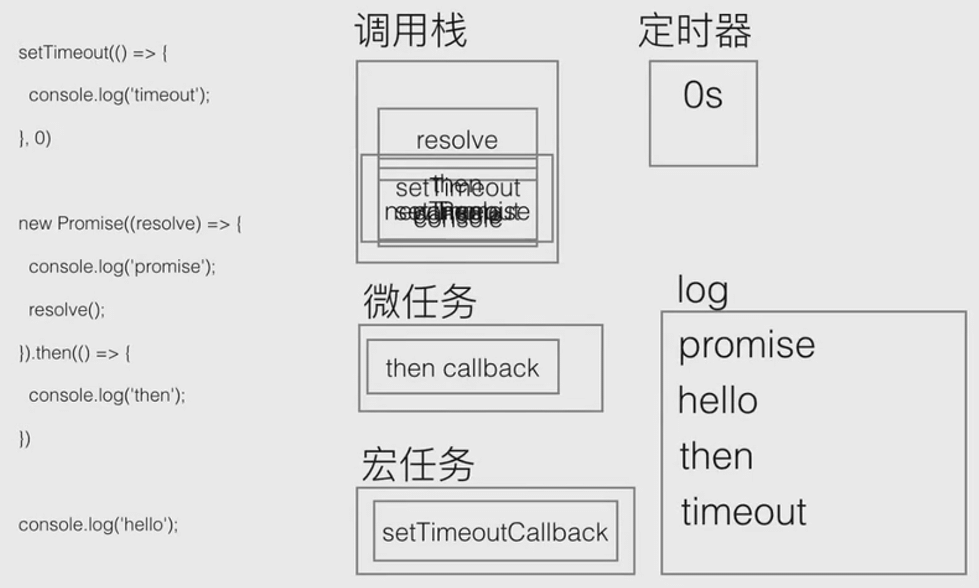
js
console.log(1);
setTimeout(function () {
console.log(2);
}, 10);
new Promise(function (resolve) {
console.log(3);
resolve();
console.log(4);
}).then(function () {
console.log(5);
});
console.log(6);
console.log(8);
requestAnimationFrame(() => console.log(9));Buffer
什么是 Buffer
- Buffer 是 UInt8Array
- 是数组, 且每个 item 有效范围是 0~255
js
Buffer.from([1, 1, 1, 1]);
Buffer.from([257, 257.5, -255, '1']);
Buffer.from('abcd');
// <Buffer 61 62 63 64>utf8 编码

Event
Event Eimtter
- on 方法, 注册事件回调
- emit 方法, 手动触发事件
js
const EventEmitter = require('events');
class MyEventEmitter extends EventEmitter {}
const myEventEmitter = new MyEventEmitter();
myEventEmitter.on('ping', function () {
console.log('pong');
});
myEventEmitter.emit('ping');Stream
什么是 Stream
- Node.js 中很多对象都是 Stream, 例如 HTTP 的请求, 进程日志输出, 文件的读写
- Stream 本身是一个 EventEmitter
- Stream 内部含有 Buffer
- 当 Stream 中 Buffer 有数据可读时, emit data 事件, 通知外部读取数据
- 当 Stream 可写时, 通过调用 write(), end() API 来写入数据到内部 Buffer 中
Stream 的类型
- 可写 Writable
- 可读 Readable
- 双工 Duplex
- 转换 Transform
Stream 的应用场景
fs.createReadStream('sample.txt', { start: 90, end: 99 })
gulp.src('**/*').pipe(xxx)
fetch('https://www.baidu.com').then(data => xxx)
js
const http = require('http');
const net = require('net');
const { URL } = require('url');
// Create an HTTP tunneling proxy
const proxy = http.createServer((req, res) => {
res.writeHead(200, {
'Content-Type': 'text/plain'
});
res.end('okay');
});
proxy.on('connect', (req, clientSocket, head) => {
// Connect to an origin server
const { port, hostname } = new URL(`http://${req.url}`);
const serverSocket = net.connect(port || 80, hostname, () => {
clientSocket.write('HTTP/1.1 200 Connection Established\r\n' +
'Proxy-agent: Node.js-Proxy\r\n' +
'\r\n');
serverSocket.write(head);
})
});Node 全局对象
常用的 Node.js 全局对象
- clearInterval
- setInterval
- clearTimeout
- setTimeout
- console
- process
全局对象与模块
- __filename
- __dirname
- exports
- module
- require
这 5 个 API 看上去像是全局对象, 但其实是在模块加载的时候进行注入, 所以要和全局对象进行区分.