MyBatis
数据信息配置
01_02
导包
==key==
- asm.jar
- cglib.jar(动态代理,spring课有讲)
- commons-logging.jar
- log4j.jar
- mybatis.jar
- mysql-connector-java.jar(数据库驱动包)
- slf4j.jar
- slf-log4j.jar
主配置文件
mybatis-config.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<!-- 环境配置 -->
<environments default="default">
<!-- 表示一个数据库环境 -->
<environment id="default">
<!--
事务管理器
JDBC: 表示一个权限定名的别名
-->
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<!--
数据源配置
POOLED: 使用mybatis中的内置连接池,表示一个别名
-->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://mybatis"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value=""/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
</configuration>保存对象
01_03
编写domain文件User.java
添加domain文件映射信息UserMapper.xml
xml<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <!-- 建议namespace:所在包名+mapper名 --> <mapper namespace="main.UserMapper"> <!-- insert表示插入操作 parameterType: 参数类型 keyColumn: 数据库中自增长字段名 keyProperty: 自增长的字段注入实体的哪个字段 useGenerateKeys: 标记这个标签需要使用数据库中的自增长id --> <insert id="save" parameterType="main.User" keyColumn="id" keyProperty="id" useGenerateKeys="true"> insert into user(userName,password,age) values (#{username},#{password},#{age}) </insert> </mapper>将domain的映射文件配置到主配置文件中
xml<mappers> <mapper resource="main.UserMapper.xml"/> </mappers>编写测试类,保存对象
java@Test public void testSave() throws Exception { User u = new User("admin","123",17); SqlSessionFactory sf = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder() .build(Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml")); Session session = sf.openSession(); session.insert("main.UserMapper.save", u);//namespace+id session.commit(); session.close(); System.out.println(u); }
补充
01_05
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">JDBC: 使用JDBC的事务管理,表示一个全限定名的别名
对应的全限定名为: org.apache.ibatis.transaction.jdbc.JdbcTransactionFactory
POOLED: 使用mybatis中的内置连接池,表示一个别名
对应的全限定名为: org.apache.ibatis.datasource.pooled.PooledDataSourceFactory
监控SQL信息的配置
01_06
资源目录下添加log4j.properties
配置log4j.properties
# Global logging configuration
log4j.rootLogger=ERROR, stdout
# MyBatis logging configuration... 这里填写namespace的包名或者父包名
log4j.logger.main=TRACE
# Console output...
log4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern=%5p [%t] - %m%n更新,查询,删除
01_07,08,09
更新
<update id="update" parameterType="main.User">
update user set username=#{userName},password=#{password},age=#{age} where id=#{id}
</update>@Test
public void testUpdate() throws Exception {
User u = new User("aw","gai",19);
Session session = MybatisUtils.openSession();
session.update("main.UserMapper.update", u);
session.commit();
session.close();
}重构SqlSession开启操作
public class MybatisUtils {
private SqlSessionFactory sf = null;
private static MybatisUtils instance = new MybatisUtils();
private MybatisUtils() {
try {
sf = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder()
.build(Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml"));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static SqlSession openSession() {
return instance.sf.openSession();
}
}查询单个
<select id="get" parameterType="java.lang.Long" resultType="main.User">
select id,username,password,age from user where id=#{id}
</select>@Test
public void testGet() throws Exception {
Session session = MybatisUtils.openSession();
User u = session.selectOne("main.UserMapper.get", 1L);
System.out.println(u);
session.close();
}查询所有
<select id="listAll" resultType="main.User">
select id,username,password,age from user
</select>@Test
public void testList() throws Exception {
Session session = MybatisUtils.openSession();
List<User> users = session.selectList("main.UserMapper.listAll");
for (User u : users)
System.out.println(u);
session.close();
}删除
<delete id="delete" parameterType="java.lang.Long">
delete from user where id=#{id}
</delete>@Test
public void testDelete() throws Exception {
Session session = MybatisUtils.openSession();
session.delete("main.UserMapper.delete",1L);
session.commit();
session.close();
}补充内容
01_10
对于普通的 Java 类型,有许多内建的类型别名。它们都是大小写不敏感的,注意原生类型的特殊处理
| 别名 | 映射的类型 |
|---|---|
| _byte | byte |
| _long | long |
| _short | short |
| _int | int |
| _integer | int |
| _double | double |
| _float | float |
| _boolean | boolean |
| string | String |
| byte | Byte |
| long | Long |
| short | Short |
| int | Integer |
| integer | Integer |
| double | Double |
| float | Float |
| boolean | Boolean |
| date | Date |
| decimal | BigDecimal |
| bigdecimal | BigDecimal |
| object | Object |
| map | Map |
| hashmap | HashMap |
| list | List |
| arraylist | ArrayList |
| collection | Collection |
| iterator | Iterator |
sqlsession的insert,delete方法底层都是调用的update方法
MyBatis和Hibernate的区别
01_11
和hibernate对比,MyBatis更基础,要求使用者自己控制的东西更多。
mybatis完成了基本的一些ORM概念,但是没有Hibernate那么完善。要使用mybatis,程序员的关注点更集中于SQL和数据库结构设计。
mybatis没有hibernate使用起来那么面向对象,所以,在使用mybatis的时候,hibernate的一些思想和设计需要改变。
MyBatis的好处:更底层,对性能控制更有优势
高级查询更方便
更新操作可以更新个别字段(hibernate还要判断是否空,如WMS前台的编辑员工未传递密码)
别名方式
01_12
mybatis-config.xml中配置
<typeAliases>
<!--
type: 需要定义别名的全限定类
alias: 定义的别名
-->
<typeAlias type="main.User" alias="User"/>
</typeAliases>使用db.properties配置数据库连接信息
01_13
db.driverClaassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
db.url=jdbc:mysql:///mybatis
db.userName=root
db.password=主配置文件更改
<property name="driver" value="${db.driverClaassName}"/>
<property name="url" value="${db.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${db.userName}"/>
<property name="password" value="${db.password}"/>方式一
SqlSessionFactory传入properties对象
javaprivate MybatisUtils() { try { Properties p = new Properties(); p.load(Resources.getResourceAsStream("db.properties")); sf = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder() .build(Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml"),p); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }方式二
主配置文件中加入properties配置
xml<properties resource="db.propesties" />
使用Mapper接口的方式定义
01_14
使用statementID的方式存在如下问题
传入的statement字符串有可能会写错,写错的时候必须等到运行的时候才发现
传入的参数无法限定类型
使用Mapper接口的方式
- 接口的全限定名==UserMapper.xml中的namespace
- 接口中方法==UserMapper.xml中标签ID
- 接口方法上的参数==UserMapper.xml中的parameterType
- 接口方法上的返回值类型==UserMapper.xml中的resultType
/* UserMapper.java */
public interface UserMapper {
void save(User u);
void update(User u);
void delete(Long id);
User get(Long id);
List<User> listAll();
}/* session.insert("main.UserMapper.save", u); */
UserMapper mapper = session.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
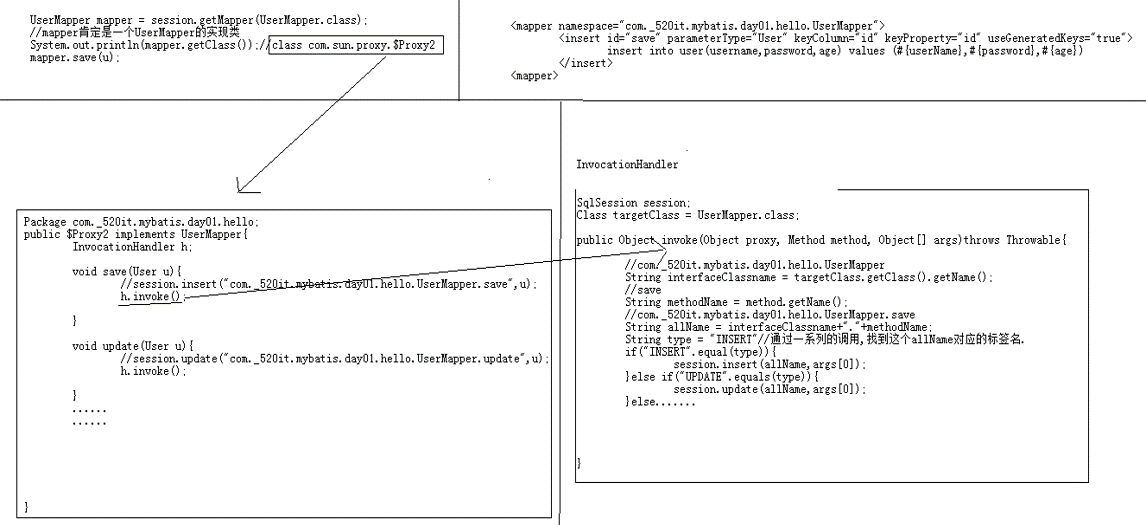
mapper.save(u);使用接口的方式源码分析
01_15
ResultMap映射
01_16
当查询出来的字段名和对象中的属性名不一致的情况,就没办法使用resultType来默认映射(同名规则)
解决方案:
使用resultMap来映射数据库中的字段到底注入到对象中什么属性中
在mapper文件中定义resultMap标签
<resultMap type="User" id="base_map">
<!--
column: 查询出来的字段名
property: 对象中的属性名
jdbcType: 数据库中字段类型
javaType: 对象属性的类型
-->
<id column="id" property="d_id" />
<result column="d_username" property="userName" />
<result column="d_password" property="password" />
<result column="d_age" property="age" />
</resultMap>
<select id="listAll" resultMap="base_map">
select d_id,d_username,d_password,d_age from user
</select>动态SQL
01_17,18,19
where
@Getter @Setter
public class QueryObject {
private String keyword;
private Integer beginAge;
private Integer endAge;
}<select id="selectByCondition" parameterType="main.QueryObject" resultType="User">
select * from user
<where>
<if test="keyword!=null">
username like '%${keyword}%'
</if>
<if test="beginAge!=null">
AND age >= #{beginAge}
</if>
<if test="endAge!=null">
AND age <= #{endAge}
</if>
</where>
</select>set
<update id="updateDy" parameterType="main.User">
update user
<set>
<if test="userName!=null">
userame=#{userName},
</if>
<if test="password!=null">
password=#{password},
</if>
<if test="age!=null">
age=#{age},
</if>
</set>
where id=#{id}
</update>foreach
<select id="queryForEach" resultType="User">
select * from user where id in
<!-- collection: list,array,map -->
<foreach collection="list" open="(" close=")" separator="," item="value">
#{value}
</foreach>
<!-- (1,2,3,4,5) -->
</select>trim
<where>等价于如下
<trim prefix="WHERE" prefixOverrides="AND|OR">
</trim>set等价于如下
<trim prefix="SET" suffixOverrides=",">
</trim>高级查询+分页
01_20
IUserService.java
public interface IUserService {
public PageResult list(QueryObject qo);
}PageResult.java
@NoArguments @AllArguments
@Getter @Setter
public class PageResult {
private Long total;
private List rows;
public static final PageResult EMPTY = new PageResult(0L,Collections.emptyList());
}QueryObject.java
@Getter @Setter
public class QueryObject {
private Long currentPage;
private Long pageSize;
private String keyword;
private Integer beginAge;
private Integer endAge;
public Long getStart() {
return (this.currentPage - 1) * this.pageSize;
}
}UserServiceImpl
public class UserServiceImpl implements IUserService {
@Override
public PageResult list(QueryObject qo) {
SqlSession session = MyBatisUtils.openSession();
UserMapper mapper = session.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
//查询总数
try{
Long count = mapper.selectByConditionCount(qo);
if (count > 0) {
List<User> result = mapper.selectByCondition(qo);
return new PageResult(count, result);
} else {
return PageResult.EMPTY;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
session.close();
}
return null;
}
}UserMapper.xml
<sql id="condition">
<where>
<if test="keyword!=null">
username like '%${keyword}%'
</if>
<if test="beginAge!=null">
AND age >= #{beginAge}
</if>
<if test="endAge!=null">
AND age <= #{endAge}
</if>
</where>
</sql>
<select id="selectByConditionCount" parameterType="main.QueryObject" resultType="long">
select count(*) from user
<include refid="condition"></include>
</select>
<select id="selectByCondition" parameterType="main.QueryObject" resultType="User">
select * from user
<include refid="condition"></include>
limit #{start},#{pageSize}
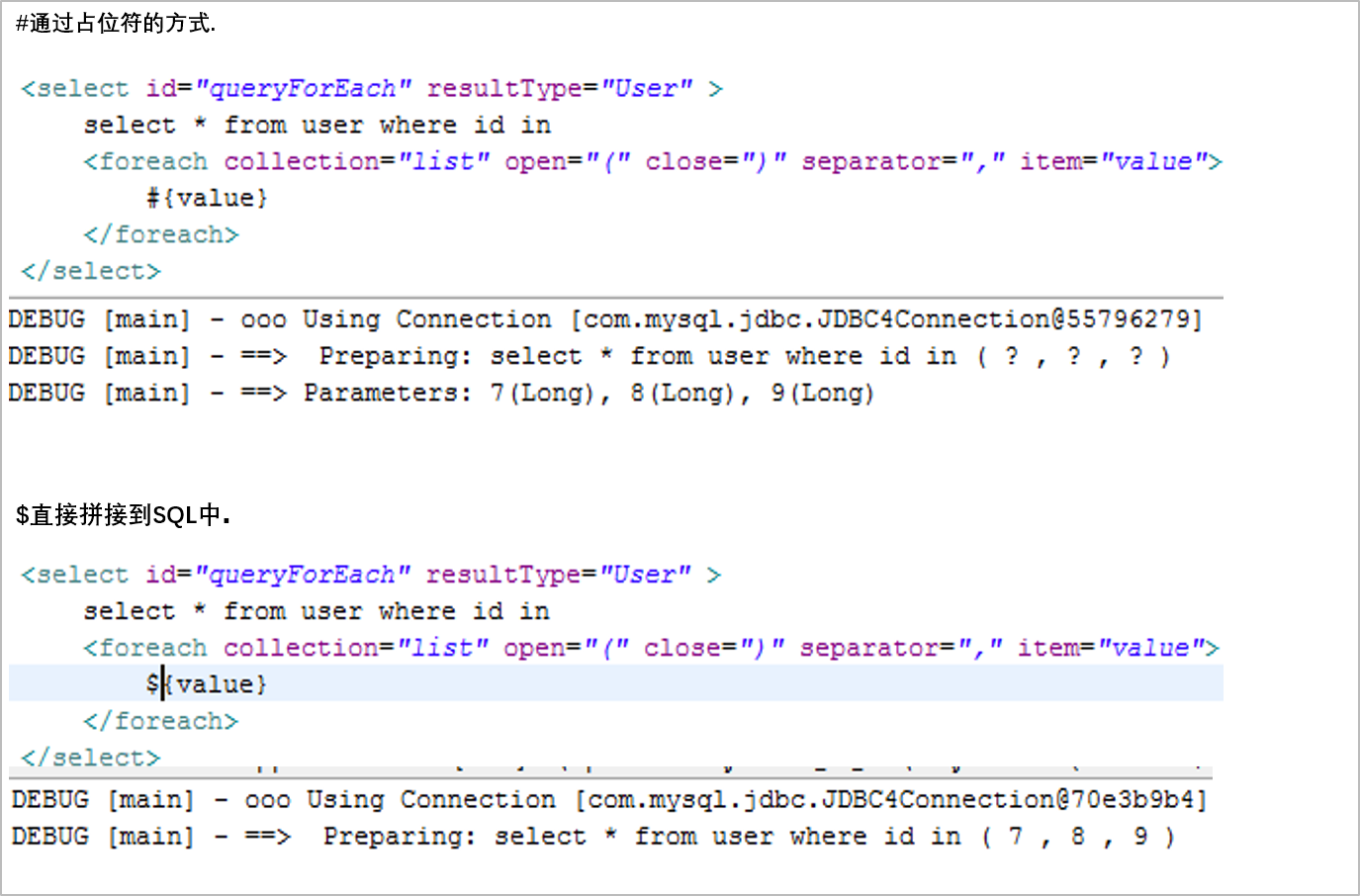
</select>$和#的区别
01_22
使用注解方式配置映射
02_01
public interface IUserDao {
@Insert("insert into user(username,password,age) values (#{username},#{password},#{age})")
@Options(keyColumn="id",keyProperty="id",useGeneratedKey="true")
void save(User u);
@Insert("update user set username=#{username},password=#{password},age=#{age} where id=#{id}")
void update(User u);
@Select("select * from user where id=#{id}")
/*
xml里配置
@ResultMap("base_map")
*/
@Results({
@Result(column="d_id",property="id"),
@Result(column="d_username",property="userName"),
@Result(column="d_password",property="password"),
@Result(column="d_age",property="age")
})
User get(Long id);
}使用@Param注解
02_02
<select id="login" resultType="User">
select * from user WHERE username = #{userName} AND password = #{password}
</select>mybatis中的方法都是只支持传入一个参数的
如果想传入多个参数
方式一:Map集合
在方法参数定义Map集合,把需要传入的参数放入map中
User login(Map<String,Object> paramMap);Map<String,Object> paramMap = new HashMap<>();
paramMap.put("userName","jack");
paramMap.put("password","234");
User u = mapper.login(paramMap);方式二:@Param注解
User login(@Param("userName") String userName,@Param("password") String password);User u = mapper.login("jack","234");原理:
@Param底层还是将参数封装成paramMap传递
单向many2one
02_03,04
Employee字段 Long id,String name,Department dept
Department字段 Long id,String name
数据库设计 employee表存在dept_id外键
保存
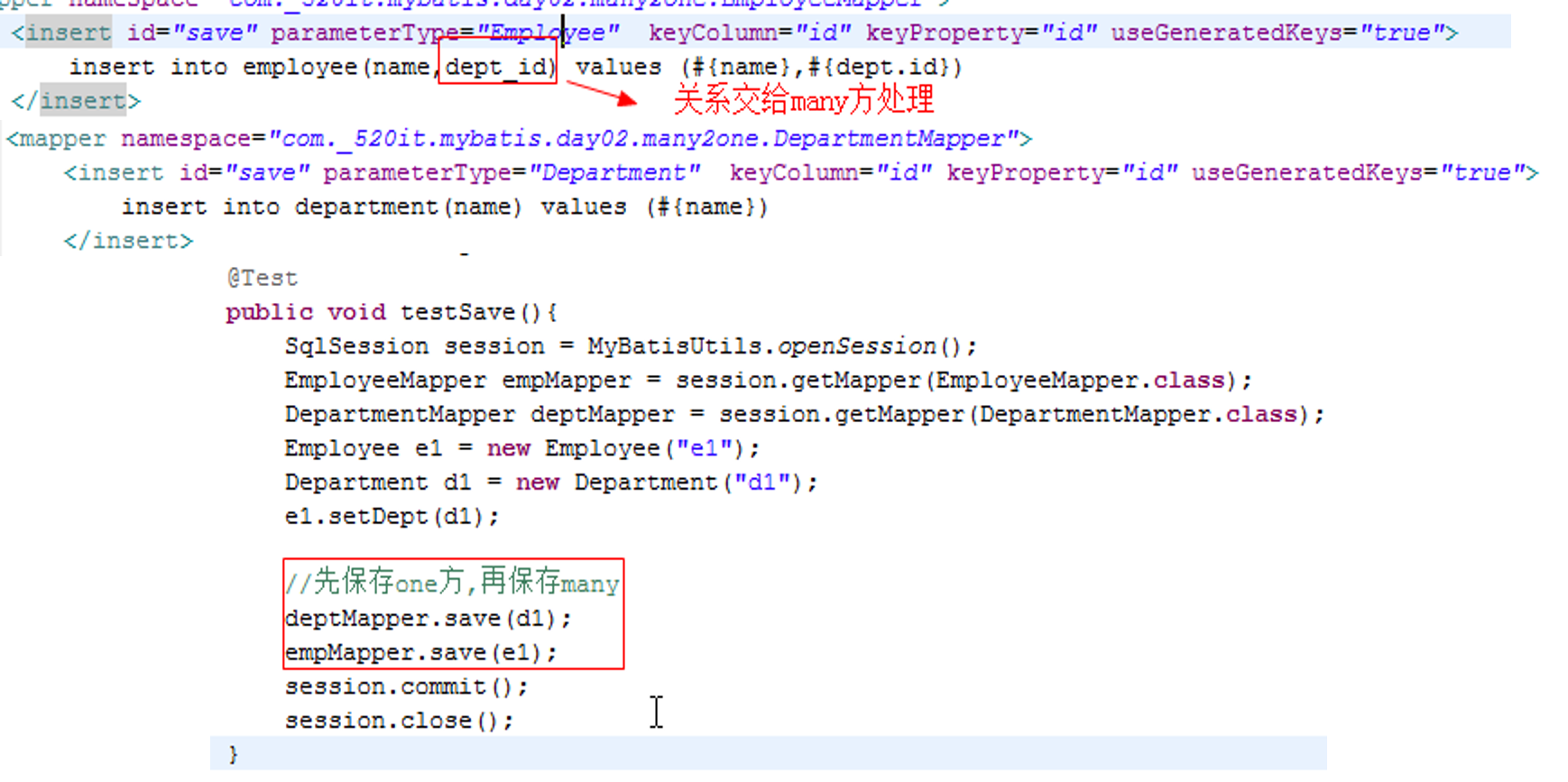
如果先保存employee(many方)
此时department(one方)还没保存,department的id属性为空,没有自动注入,所以数据库中的dept_id为null
查询
查询employee(many方)
<resultMap id="base_map" type="main.entity.Employee">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<association colomn="dept_id" property="dept" javaType="main.entity.Department"
select="main.DepartmentMapper.get">
</association>
</resultMap>
<select id="get" resultMap="base_map">
select id,name,dept_id from employee where id = #{id}
</select>association中的属性
property 表示实体类中的关联关系属性名
javaType 实体类类型
select 标识需要发送sql去查询出关联对象的sql映射
column 需要发送sql查询关联对象的查询条件参数
延迟加载
02_05
回顾hibernate中的延时加载
many方是正常的对象,one是代理代理
当调用one的非ID和非Class属性的时候才去调用session去查询出结果出来
mybatis中的延时加载
在myBatis中默认的延时加载时禁用的
在主配置文件中开启延时加载 - lazyLoadingEnabled
xml<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/>many变成代理对象.class
com._520it.mybatis.day02.many2one.Employee$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$42c5091f
调用many方的任意属性,都会触发one方的加载
aggressiveLazyLoading:当启用时, 有延迟加载属性的对象在被调用时将会完全加载任意属性。否则, 每种属性将会按需要加载
xml<!-- 配置如下属性,按需加载 --> <setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false"/>在many方默认的调用equals,clone,hashCode,toString 方法都会出发one方的加载
xml<!-- 配置只有调用many方的clone方法才会触发one方加载, 默认为"equals,clone,hashcode,toString" --> <setting name="lazyLoadTriggerMethods" value="clone"/>
N + 1 问题的解决方案
02_06
在查询所有many记录,每个many对应的one都是不同,查询N个many对象
总共会发出N+1条SQL(性能特别不友好)
使用连接查询
<resultMap id="base_map" type="main.entity.Employee">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<association property="dept" javaType="main.entity.Department">
<id column="dept_id" property="id"/>
<result column="dept_name" property="name"/>
</association>
</resultMap>
<select id="list" resultMap="base_map">
select e.id,e.name,d.id as dept_id,d.name as dept_name from employee e left join department d on e.dept_id=d.id
</select>补充
02_07
columnPrefix 为one方映射设置统一前缀
<association property="dept" javaType="main.entity.Department" columnPrefix="dept_">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
</association>一级缓存
02_08
生命周期
和session一样的生命周期
通过
session.get(1L),session.get(1L),总共两次get方法只会发一条SQL.第二次使用的是一级缓存的内容
针对数据量大的时候,使用分页+clearCache()及时清除缓存
//清除一级缓存中内容
session.clearCache();单向one2many
02_09,10,11,12
Employee字段 Long id,String name
Department字段 Long id,String name,List<Employee> emps
数据库设计 employee表存在dept_id外键
保存
EmployeeMapper.xml
<insert id="save" parameterType="main.entity.Employee"
keyColumn="id" keyProperty="id" useGeneratedKeys="true">
insert into employee(name) values (#{name})
</insert>DepartmentMapper.xml
<insert id="save" parameterType="main.entity.Department"
keyColumn="id" keyProperty="id" useGeneratedKeys="true">
insert into department(name) values(#{name})
</insert>
<update id="handlerRelation">
update employee set dept_id=#{deptID} where id=#{empID}
</update>DepartmentMapper.java
void handlerRelation(@Param("deptID") String deptID,@Param("empID") String empID);testSave
@Test
public void testSave() {
SqlSession session = MyBatisUtils.openSession();
EmployeeMapper empMapper = session.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);
DepartmentMapper deptMapper = session.getMapper(DepartmentMapper.class);
Employee e1 = new Employee("e1");
Employee e2 = new Employee("e2");
Department d1 = new Department("d1");
d1.getEmps().add(e1);
d1.getEmps().add(e2);
deptMapper.save(d1);
empMapper.save(e1);
empMapper.save(e2);
//由one方去处理外键关系
for (Employee emp : d1.getEmps())
deptMapper.handlerRelation(d1.getId(), emp.getId());
session.commit();
session.close();
}查询
DepartmentMapper.xml
<resultMap id="base_map" type="main.entity.Department">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<collection column="id" property="emps" ofType="main.entity.Employee"
select="main.mapper.EmployeeMapper.selectByDeptId">
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="get" parameterType="long" reultMap="base_map">
select * from department where id=#{id}
</select>EmployeeMapper.xml
<select id="selectByDeptId" parameterType="long" resultType="main.entity.Employee">
select id,name from employee where dept_id=#{deptId}
</select>查询 - 内联方式
02_11
<resultMap id="base_map" type="main.entity.Department">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<collection property="emps" ofType="Employee" columnProfix="emp_">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="get" parameterType="long" reultMap="base_map">
select d.id,d.name,e.id as emp_id,e.name as emp_name
from department d
left join employee e on e.dept_id=d.id
where d.id=#{id}
</select>删除
02_12
DepartmentMapper.xml
<delete id="delete" parameterType="long">
delete from department where id=#{id}
</delete>EmployeeMapper.xml
<update id="updateRelation" parameterType="long">
update employee set dept_id=null where dept_id=#{deptId}
</update>testDelete
@Test
public void testSave() {
SqlSession session = MyBatisUtils.openSession();
EmployeeMapper empMapper = session.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);
DepartmentMapper deptMapper = session.getMapper(Department.class);
//删除之前先处理外键约束
Department department = deptMapper.get(17L);
empMapper.updateRelation(17L);
deptMapper.delete(17L);
session.commit();
session.close();
}many2many
02_13,14
Teacher字段 Long id,String name,List<Student> stus
Student字段 Long id,String name
数据库设计 中间表
保存
TeacherMapper.xml
<insert id="save" parameterType="main.entity.Teacher"
keyColumn="id" keyProperty="id" useGeneratedKeys="true">
insert into teacher(name) values (#{name})
</insert>
<insert id="handlerRelation">
insert into tea_stu(t_id,s_id) values(#{teaId},#{stuId})
</insert>StudentMapper.xml
<insert id="save" parameterType="main.entity.Student"
keyColumn="id" keyProperty="id" useGeneratedKeys="true">
insert into student(name) values (#{name})
</insert>TeacherMapper.java
void handlerRelation(@Param("teaId") String teaId,@Param("stuId") String stuId);testSave
@Test
public void testSave() {
//准备数据
Teacher t1 = new Teacher("t1"); Teacher t2 = new Teacher("t2");
Student s1 = new Student("s1"); Student s2 = new Student("s2");
t1.getStus().add(s1); t1.getStus().add(s2);
t2.getStus().add(s1); t2.getStus().add(s2);
SqlSession session = MyBatisUtils.openSession();
TeacherMapper teaMapper = session.getMapper(TeacherMapper.class);
StudentMapper stuMapper = session.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
teaMapper.save(t1); teaMapper.save(t2);
stuMapper.save(s1); stuMapper.save(s2);
//处理中间表的关系
for(Student stu : t1.getStus())
teaMapper.handleRelation(t1.getId(), stu.getId());
for(Student stu : t2.getStus())
teaMapper.handleRelation(t2.getId(), stu.getId());
session.commit();
session.close();
}查询
TeacherMapper.xml
<resultMap id="base_map" type="main.entity.Teacher">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<collection column="id" property="stus" ofType="main.entity.Student"
select="main.mapper.StudentMapper.selectByTId">
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="get" parameterType="long" reultMap="base_map">
select * from teacher where id=#{id}
</select>StudentMapper.xml
<select id="selectByTId" parameterType="long" resultType="main.entity.Student">
select id,name from student where id in (select s_id from tea_stu where t_id in(select t_id from teacher where id=#{tId}))
</select>查询 - 内联方式
<resultMap id="base_map" type="main.entity.Teacher">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<collection property="stus" ofType="main.entity.Student" columnProfix="stu_">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="get" parameterType="long" reultMap="base_map">
select t.id,t.name,s.id as stu_id,s.name as stu_name
from teacher t
left join tea_stu m on t.id=m.t_id
left join student s on s.id=m.s_id
where t.id=#{id}
</select>回顾Hibernate的二级缓存
02_17
二级缓存的生命周期和sessionFactory一样的生命周期
什么样类型的对象适合放入二级缓存
读远远大于写的对象
hibernate中的缓存
一级缓存
二级缓存
查询缓存(限制很多,命中率比较低)
开启二级缓存后,get (),insert(),get(); 总共发2条sql
insert()不会影响到二级缓存,会影响查询缓存
MyBatis中的(二级)缓存
02_18
启用MyBatis缓存
需要在mapper文件中添加
<cache />缓存的对象需要实现序列化接口
myBatis开启二级缓存后,get(),insert(),get(); 总共发3条sql
在mybatis中无论是selectOne还是selectList都是使用查询缓存
当对象新增,更新,删除的时候,都会去清空查询缓存
手动让MyBatis缓存向hibernate 二级缓存靠近
list(查询)方法不去缓存中存放对象
xml<select id="list" resultType="main.entity.User" useCache="false"> select * from User </select>insert(新增)方法不去清空缓存
xml<insert id="save" parameterType="main.entity.User" keyColumn="id" keyProperty="id" useGeneratedKeys="true" flushCache="false"> insert into user(username,password,age) values(#{userName},#{password},#{age}) </insert>
使用第三方缓存框架
02_19
导包
- ehcache-core.jar
- mybatis-ehcache.jar
添加ehcache.xml配置文件
在mapper文件中配置
xml<cache type=”org.mybatis.caches.ehcache.EhcacheCache”>使用不同的缓存策略,在ehcache.xml中配置
xml<cache name="Mapper文件中的namespace" maxElementsInMemory="100" eternal="true" timeToIdleSeconds="300" timeToLiveSeconds="600" overflowToDisk="true" />maxElementsInMemory:该缓存池放在内存中最大的缓存对象个数
eternal:是否永久有效,如果设置为true,内存中对象永不过期
timeToIdleSeconds:缓存对象最大空闲时间,单位:秒
timeToLiveSeconds:缓存对象最大生存时间,单位:秒
overflowToDisk:当内存中对象超过最大值,是否临时保存到磁盘
maxElementsOnDisk:能保存到磁盘上最大对象数量
diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds:磁盘失效线程运行时间间隔,默认是120秒
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy:当达到maxElementsInMemory限制时,Ehcache将会根据指定的策略去清理内存